FDA is talking about breast implants and the danger that comes along with them. First, they said that they are restricting the sale of breast implants because they are harmful to the people and that the people who are making decisions should be the one who is going to be well informed about it.
The risks and the benefits should be both known or rather made known to the people who are opting for breast implants. The FDA now had provided labeling to the new and the best kind of breast implants that are relatively safer and legal.
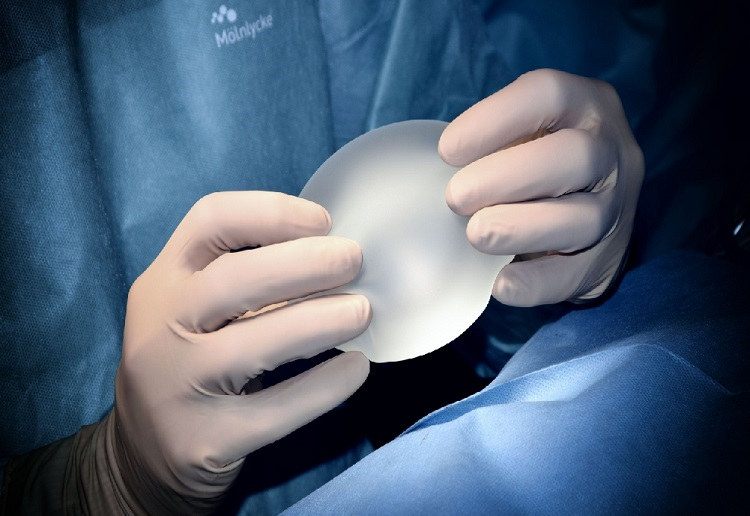
The FDA labeling is something that one needs to look at before they get breast implants. It is said that the labeling includes several of the boxed warnings that come with the category of the thing, it also includes a patient device card, and as well as a device description which is given to the person along with a list of specific materials that had been used in the device.
Nevertheless, except for all of that, we get the updated silicone gel-filled breast implant rupture screening recommendations and a patient decision checklist. The last thing is a must thing to have as it is a checklist that must be reviewed with the patient. That is an absolute necessity.
This is the checklist that the doctor or the health care providers are going to clear with the patients first since it is highly obliged to do so and make the patient aware of the risk, benefits, and some other additional details about the breast implants.
Things that are crucial for knowing before the surgery. The checklist that is provided also needs to be signed by the patient. It also required the signature of the physician that is implanting the device in the person.
That’s the call that FDA had been making and now it wants the providers to change and adapt to the guidelines as soon as possible. There is a time limit of one month given to them. We hope that you are aware that we will bring you the news as well.


